本文介绍Nginx+PHP+MySQL双机互备、故障自动切换方案,希望对于初学Nginx服务器相关的朋友有帮助,更多Nginx安装、配置、报错处理等资源请本站内搜索。。
在生产应用中,某台“Nginx+PHP+MySQL”接口数据服务器,扮演的角色十分重要,如果服务器硬件或Nginx、MySQL发生故障,而短时间内无法恢复,后果将非常严重。为了避免单点故障,我设计了此套方案,编写了failover.sh脚本,实现了双机互备、全自动切换,故障转移时间只需几十秒。
一、双机互备、全自动切换方案:1、拓扑图:
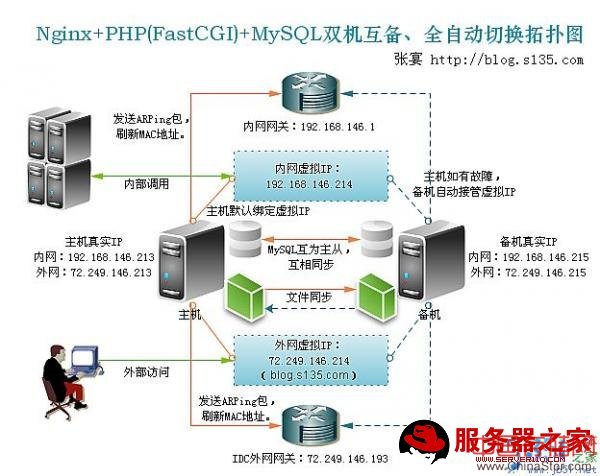
2、解释:
(1)、假设外网域名blog.s135.com解析到外网虚拟IP 72.249.146.214上,内网hosts设置db10对应内网虚拟IP 192.168.146.214
(2)、默认情况下,由主机绑定内、外网虚拟IP,备机作为备份,当主机的MySQL、Nginx或服务器出现故障无法访问时,备机会自动接管内、外网虚拟IP。两台服务器都启动负责监控、自动切换虚拟IP的守护进程/usr/bin/nohup /bin/sh /usr/local/webserver/failover/failover.sh 2>&1 > /dev/null &
(3)、主机和备机上的MySQL服务器互为主从,互相同步。在主机处于活动状态(即由主机绑定虚拟IP)时,读写主机的MySQL,写到主机的数据会同步到备机;在备机处于活动状态时,读写备机的MySQL,写到备机的数据会同步到主机(如果主机上的MySQL死掉暂时无法同步,主机上的MySQL恢复后,数据会自动从备机上同步过来,反之亦然)。
(4)、主机处于活动状态时,每20秒会把/data0/htdocs/(网页、程序、图片存放目录)、/usr/local/webserver/php/etc/(php.ini等配置文件目录)、/usr/local/webserver/nginx/conf/(Nginx配置文件目录)三个目录下的文件通过rsync推送到备机服务器上的对应目录(增量推送,两台服务器上一样的文件不会重复推送),反之如果备机处于活动状态时,每20秒会尝试把文件推送到主机。rsync的配置文件见两台服务器的/etc/rsyncd.conf,rsync守护进程的启动命令为rsync --daemon
3、自动切换流程
(1)、主机默认绑定内、外网虚拟IP,当主机的MySQL、Nginx无法访问或服务器宕机,主机上的failover.sh守护进程会自动摘除自己绑定的内、外网虚拟IP(如果主机上的failover.sh死掉,无法摘除自己绑定的虚拟IP也没关系),备机上的failover.sh守护进程会自动接管备机原来绑定的内、外网虚拟IP,并发送ARPing包给内、外网网关更新MAC,强行接管。
(2)、备机绑定虚拟IP后,会发送ARPing包给内、外网网关,通知网关更新虚拟IP的MAC地址为备机的MAC地址,从而保证了切换后能够通过虚拟IP及时访问到备机。
(3)、如果主机的MySQL、Nginx启动起来,全部恢复正常访问,主机上的failover.sh守护进程会检测主机上的MySQL数据是否已经完全从备机上同步过来。如果同步延迟时间为0,主机会自动接管内、外网虚拟IP,并发送ARPing包给内、外网网关,而备机也会自动摘除内、外网虚拟IP。
(4)、整个切换流程均由failover.sh自动完成,无需人工处理。
4、注意事项(很重要):
(1)、crontab里的文件没有做自动同步,如果修改,需要手工在两台服务器上都做修改。
(2)、/data0/htdocs/目录内任何用ln -s建立的软连接,rsync不会自动同步,如果在一台服务器上建了软连接,需要手工在另外一台服务器上也建相同的软连接。
(3)、如果要删除/data0/htdocs/目录内的某些文件或目录,需要先删除处于活动状态(即绑定了虚拟IP)服务器上的文件或目录,再删除处于备用状态服务器上的文件或目录。
(4)、除了/data0/htdocs/(网页、程序、图片存放目录)、/usr/local/webserver/php/etc/(php.ini等配置文件目录)、/usr/local/webserver/nginx/conf/(Nginx配置文件目录)三个目录之外的其他配置修改,需要在两台服务器上都做修改。
二、配置文档与脚本:
1、主机、备机两台服务器的rsync配置(配置相同)
(1)、rsync配置文件
vi /etc/rsyncd.conf 输入一些内容并保存:uid = root
gid = root
use chroot = no
max connections = 20
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
[data0_htdocs]
path = /data0/htdocs/
ignore errors
read only = no
hosts allow = 192.168.146.0/24
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32
[php_etc]
path = /usr/local/webserver/php/etc/
ignore errors
read only = no
hosts allow = 192.168.146.0/24
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32
[nginx_conf]
path = /usr/local/webserver/nginx/conf/
ignore errors
read only = no
hosts allow = 192.168.146.0/24
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32
2)、启动rsync守护进程/usr/bin/rsync --daemon
2、两台MySQL互为主从的配置
这里就不详细写出互为主从的配置过程了,如果不懂的朋友可以在Google上搜一下。有一点需要指出,my.cnf配置文件中请加上skip-name-resolve参数,使用IP来进行MySQL帐号验证。
3、主机、备机两台服务器负载监控、虚拟IP自动切换的failover.sh守护进程
(1)、启动failover.sh守护进程(为了开机能够自动运行,请将以下语句添加到/etc/rc.local文件中):
/usr/bin/nohup /bin/sh /usr/local/webserver/failover/failover.sh 2>&1 > /dev/null &
(2)、停止failover.sh守护进程:
ps -ef | grep failover.sh
会显示以下信息:
root 15428 1 0 Nov17 ? 00:00:03 /bin/sh /usr/local/webserver/failover/failover.sh
root 20123 6878 0 16:16 pts/2 00:00:00 grep failover.sh
然后杀死failover.sh的进程:
kill -9 15428
(3)、failover.sh代码内容(请注意其中的type设置,主机设为master,备机设为slave):
#!/bin/shLANG=C
date=$(date -d "today" +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
#---------------配置信息(开始)---------------
#类型:主机设为master,备机设为slave
type="master"
#主机、备机切换日志路径
logfile="/var/log/failover.log"
#MySQL可执行文件地址,例如/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql;MySQL用户名;密码;端口
mysql_bin="/usr/local/webserver/mysql/bin/mysql"
mysql_username="root"
mysql_password="123456"
mysql_port="3306"
#内网网关
gateway_eth0="192.168.146.1"
#主机内网真实IP
rip_eth0_master="192.168.146.213"
#备机内网真实IP
rip_eth0_slave="192.168.146.215"
#主机、备机内网共用的虚拟IP
vip_eth0_share="192.168.113.214"
#外网网关
gateway_eth1="72.249.146.193"
#主机外网真实IP
rip_eth1_master="72.249.146.213"
#备机外网真实IP
rip_eth1_slave="72.249.146.215"
#主机、备机外网共用的虚拟IP
vip_eth1_share="72.249.146.214"
#---------------配置信息(结束)---------------
#绑定内、外网虚拟IP
function_bind_vip()
{
/sbin/ifconfig eth0:vip ${vip_eth0_share} broadcast ${vip_eth0_share} netmask 255.255.255.255 up
/sbin/route add -host ${vip_eth0_share} dev eth0:vip
/sbin/ifconfig eth1:vip ${vip_eth1_share} broadcast ${vip_eth1_share} netmask 255.255.255.255 up
/sbin/route add -host ${vip_eth1_share} dev eth1:vip
/usr/local/webserver/php/sbin/php-fpm reload
kill -USR1 `cat /usr/local/webserver/nginx/logs/nginx.pid`
/sbin/service crond start
}
#解除内、外网虚拟IP
function_remove_vip()
{
/sbin/ifconfig eth0:vip ${vip_eth0_share} broadcast ${vip_eth0_share} netmask 255.255.255.255 down
/sbin/ifconfig eth1:vip ${vip_eth1_share} broadcast ${vip_eth1_share} netmask 255.255.255.255 down
/sbin/service crond stop
}
#主机向备机推送文件的函数
function_rsync_master_to_slave()
{
/usr/bin/rsync -zrtuog /data0/htdocs/ ${rip_eth0_slave}::data0_htdocs/ > /dev/null 2>&1
/usr/bin/rsync -zrtuog /usr/local/webserver/php/etc/ ${rip_eth0_slave}::php_etc/ > /dev/null 2>&1
/usr/bin/rsync -zrtuog /usr/local/webserver/nginx/conf/ ${rip_eth0_slave}::nginx_conf/ > /dev/null 2>&1
}
#备机向主机推送文件的函数
function_rsync_slave_to_master()
{
/usr/bin/rsync -zrtuog /data0/htdocs/ ${rip_eth0_master}::data0_htdocs/ > /dev/null 2>&1
/usr/bin/rsync -zrtuog /usr/local/webserver/php/etc/ ${rip_eth0_master}::php_etc/ > /dev/null 2>&1
/usr/bin/rsync -zrtuog /usr/local/webserver/nginx/conf/ ${rip_eth0_master}::nginx_conf/ > /dev/null 2>&1
}
#虚拟IP ARPing
function_vip_arping()
{
/sbin/arping -I eth0 -c 3 -s ${vip_eth0_share} ${gateway_eth0} > /dev/null 2>&1
/sbin/arping -I eth1 -c 3 -s ${vip_eth1_share} ${gateway_eth1} > /dev/null 2>&1
}
while true
do
#用HTTP协议检查虚拟IP
if (curl -m 30 -G http://${vip_eth1_share}/ > /dev/null 2>&1) && (${mysql_bin} -u"${mysql_username}" -p"${mysql_password}" -P"${mysql_port}" -h"${vip_eth0_share}" -e"show slave statusG" > /dev/null 2>&1)
then
#取得与内网VIP绑定的服务器内网IP
eth0_active_server=$(${mysql_bin} -u"${mysql_username}" -p"${mysql_password}" -P"${mysql_port}" -h"${vip_eth0_share}" -e"show slave statusG" | grep "Master_Host" | awk -F ': ' '{printf $2}')
#如果内网VIP=主机内网IP(主机MySQL中的Master_Host显示的是备机的域名或IP),且本机为主机
if [ "${eth0_active_server}" = "${rip_eth0_slave}" ] && [ "${type}" = "master" ]
then
function_rsync_master_to_slave
function_vip_arping
#如果内网VIP=备机内网IP(备机MySQL中的Master_Host显示的是主机的域名或IP)
elif [ "${eth0_active_server}" = "${rip_eth0_master}" ]
then
if (curl -m 30 -G http://${rip_eth1_master}/ > /dev/null 2>&1) && (${mysql_bin} -u"${mysql_username}" -p"${mysql_password}" -P"${mysql_port}" -h"${rip_eth0_master}" -e"show slave statusG" | grep "Seconds_Behind_Master: 0" > /dev/null 2>&1)
then
#如果主机能够访问,数据库同步无延迟,且本机就是主机,那么由本机绑定虚拟IP
if [ "${type}" = "master" ]
then
#如果本机为主机
function_bind_vip
function_vip_arping
echo "${date} 主机已绑定虚拟IP!(Type:1)" >> ${logfile}
else
#如果本机为备机
function_remove_vip
echo "${date} 备机已去除虚拟IP!(Type:2)" >> ${logfile}
fi
else
if [ "${type}" = "slave" ]
then
#如果本机为备机
function_rsync_slave_to_master
function_vip_arping
fi
fi
fi
else
#虚拟IP无法访问时,判断主机能否访问
if (curl -m 30 -G http://${rip_eth1_master}/ > /dev/null 2>&1) && (${mysql_bin} -u"${mysql_username}" -p"${mysql_password}" -P"${mysql_port}" -h"${rip_eth0_master}" -e"show slave statusG" > /dev/null 2>&1)
then
#如果主机能够访问,且本机就是主机,那么由本机绑定虚拟IP
if [ "${type}" = "master" ]
then
function_bind_vip
function_vip_arping
echo "${date} 主机已绑定虚拟IP!(Type:3)" >> ${logfile}
else
function_remove_vip
echo "${date} 备机已去除虚拟IP!(Type:4)" >> ${logfile}
fi
elif (curl -m 30 -G http://${rip_eth1_slave}/ > /dev/null 2>&1) && (${mysql_bin} -u"${mysql_username}" -p"${mysql_password}" -P"${mysql_port}" -h"${rip_eth0_slave}" -e"show slave statusG" > /dev/null 2>&1)
then
#如果主机不能访问而备机能够访问,且本机就是备机,那么由备机绑定虚拟IP
if [ "${type}" = "slave" ]
then
function_bind_vip
function_vip_arping
echo "${date} 备机已绑定虚拟IP!(Type:5)" >> ${logfile}
else
function_remove_vip
echo "${date} 主机已去除虚拟IP!(Type:6)" >> ${logfile}
fi
else
echo "${date} 主机、备机全部无法访问!(Type:7)" >> ${logfile}
fi
fi
#每次循环暂停20秒(即间隔20秒检测一次)
sleep 20
done
声明: 此文观点不代表本站立场;转载须要保留原文链接;版权疑问请联系我们。