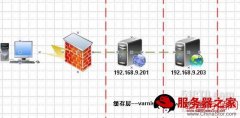
本文介绍Varnish服务器配置,希望对于Varnish入门者给与帮助。更多Varnish资源请本站内搜索。
varnish配置
配置文件的最顶端如下:
# backend default {
#.host = "127.0.0.1";
#.port = "8080";
#}
我们取消前面的注释。如下
backend default {
.host = "127.0.0.1";
.port = "8080"; #逻辑服务器apache的端口
}
varnishd启动
./varnishd -f /usr/local/varnish-3.0.2/etc/varnish/default.vcl -s malloc,1G -T 127.0.0.1:2000 -a 0.0.0.0:80
#此处的80端口是varnish工作的监听端口
/*********以下说明*********/
我添加了一些选项,现在来详细分析他们:
-f /usr/local/varnish-3.0.2/etc/default.vcl
这个 –f 选项指定 varnishd 使用哪个配置文件。
-s malloc,1G
这个 –s 选项用来确定 varnish 使用的存储类型和存储容量,我使用的是 malloc 类型(malloc 是一个 C 函数,用于分配内存空间) 1G 定义多少内存被 malloced,1G =1gigabyte。
-T 127.0.0.1:2000
Varnish 有一个基于文本的管理接口,启动它的话可以在不停止 varnish 的情况下来管理 varnish。您可以指定管理软件监听哪个接口。当然您不能让全世界的人都能访问您的varnish 管理接口,因为他们可以很轻松的通过访问 varnish 管理接口来获得您的 root 访问权限。我推荐只让它监听本机端口。如果您的系统里有您不完全信任的用户,您可以通过防火墙规则来限制他访问 varnish 的管理端口。
-a 0.0.0.0:80
这一句的意思是制定 varnish 监听所有 IP 发给 80 端口的 http 请求,如果在生产环境下,您应该让 varnish 监听 80,这也是默认的。(让varnish工作在80端口)
/*********以上说明*********/
Varnistop
您可以使用varnishtop确定哪些URL经常命中后端。
Varnishtop –i txurl 就是一个基本的命令。您可以通过阅读“Statistics”了解其他示例。
Varnishlog
当您需要鉴定哪个URL被频繁的发送到后端服务器,您可以通过varnishlog对请求做一个全面的分析。
varnishlog –c –o /foo/bar 这个命令将告诉您所有(-o)包含”/football/bar”字段来自客户端
varnishncsa
启动 varnishncsa,用来将Varnish访问日志写入日志文件:
varnishncsa -a -w /usr/local/varnish/logs/varnish.log &
如何使varnish不重启使配置文件生效
varnish服务启动脚本:
./varnishd -f ../etc/varnish/default.vcl -s malloc,1G -T 127.0.0.1:2000
注意:1、varnish服务本身,启动默认端口80;如果需要重新指定启动的端口使用 -a选项 ,如-a 0.0.0.0:8080
2、-T 选项指定了varnish服务本身的管理端口,正是利用这个端口完成一些不关闭varnish服务而使新配置生效。
方法:
1、登陆到管理接口:
>telnet 127.0.0.1 2000
>help (利用该命令可以得到很多的修改帮助)
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to 127.0.0.1.
Escape character is '^]'.
200 205
-----------------------------
Varnish Cache CLI 1.0
-----------------------------
Linux,3.0.0-12-generic,x86_64,-smalloc,-smalloc,-hcritbit
Type 'help' for command list.
Type 'quit' to close CLI session.
help
200 401
help [command]
ping [timestamp]
auth response
quit
banner
status
start
stop
vcl.load <configname> <filename>
vcl.inline <configname> <quoted_VCLstring>
vcl.use <configname>
vcl.discard <configname>
vcl.list
vcl.show <configname>
param.show [-l] [<param>]
param.set <param> <value>
panic.show
panic.clear
storage.list
ban.url <regexp>
ban <field> <operator> <arg> [&& <field> <oper> <arg>]...
ban.list
使用命令
vcl.load new.vcl /data1/varnish/etc/varnish/new.vcl (编译出错的话会有提示,成功会返回200)
200
然后使用
vcl.use new.vcl(成功后同样会返回200)
200
此时新的配置文件已经生效!
动态加载配置文件
# /opt/varnish/bin/varnishadm -T 192.168.0.125:3500
vcl.load vcl-name "配置文件路径" // vcl-name 这里可以任意取名
vcl.use vcl-name
vcl.show vcl-name //显示 vcl-name 配置文件内容
Varnish 缓存清除
# telnet 127.0.0.1 2000
ban.url test.php//清除该url的
ban.url .*//清除所有的
/**
#/opt/varnish/bin/varnishadm -T 127.0.0.1:2000 ban "req.http.host ~
www.bbs.com$ && req.url ~ /static/image/tt.jpg"
说明:
127.0.0.1:2000 //为被清除缓存服务器地址
www.bbs.com //为被清除的域名
/static/image/tt.jpg //为被清除的 url 地址列表
*/
清除所有缓存
# /opt/varnish/bin/varnishadm -T 127.0.0.1:3500 ban.url *$
清除 image 目录下所有缓存
# /opt/varnish/bin/varnishadm -T 127.0.0.1:3500 ban.url test.php.url /images
配置文件说明
当 vcl_recv 函数接收到请求时,它要判断如何处理这个请求。有三种情况 :
1)调用 pass 函数,从后端服务器调用数据。
2)调用 pipe 函数,建立客户端和后端服务器之间的直接连接,从后端服务器调用数据。
3)调用lookup函数,从缓存中查找应答数据并返回,如果查找不到,则调用pass函数从后端服务器调用数据 。
二、varnish内置的例程
vcl_recv
有请求到达后成功接收并分析时被调用,一般以以下几个关键字结束。
error code [reason] 返回code给客户端,并放弃处理该请求
pass 进入pass模式,把控制权交给vcl_pass
pipe 进入pipe模式,把控制权交给vcl_pipe
lookup 在缓存里查找被请求的对象,根据查找结果把控制权交给vcl_hit或vcl_miss
vcl_pipe
进入pipe模式时被调用。请求被直接发送到backend,后端和客户端之间的后继数据不进行处理,只是简单传递,直到一方关闭连接。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
error code [reason]
pipe
vcl_pass
进入pass模式时被调用。请求被送到后端,后端应答数据送给客户端,但不进入缓存。同一连接的后继请求正常处理。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
error code [reason]
pass
vcl_hash
目前不使用
vcl_hit
在lookup以后如果在cache中找到请求的内容事调用。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
error code [reason]
pass
deliver 将找到的内容发送给客户端,把控制权交给vcl_deliver.
vcl_miss
lookup后但没有找到缓存内容时调用,可以用于判断是否需要从后端服务器取内容。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
error code [reason]
pass
fetch 从后端取得请求的内容,把控制权交给vcl_fetch.
vcl_fetch
从后端取得内容后调用。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
error code [reason]
pass
insert 将取到的内容插入缓存,然后发送给客户端,把控制权交给vcl_deliver
vcl_deliver
缓存内容发动给客户端前调用。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
error code [reason]
deliver 内容发送给客户端
vcl_timeout
在缓存内容到期前调用。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
fetch 从后端取得该内容
discard 丢弃该内容
vcl_discard
由于到期或者空间不足而丢弃缓存内容时调用。一般以以下几个关键字结束。
discard 丢弃
keep 继续保留在缓存里
如果这些内置例程没有被定义,则执行缺省动作
附录:default.vcl
backend www {
.host = "127.0.0.1";
.port = "8080";
}
backend bbs {
.host = "127.0.0.1";
.port = "8080";
}
# Below is a commented-out copy of the default VCL logic. If you
# redefine any of these subroutines, the built-in logic will be
# appended to your code.
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.http.host ~ "(www.)?bbs.com$") {
set req.backend = bbs;
} else {
set req.backend = www;
}
#获取客户端真实IP
if (req.restarts == 0) {
if (req.http.x-forwarded-for) {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For =
req.http.X-Forwarded-For + ", " + client.ip;
} else {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip;
}
}
#Web 服务器指明不缓存的内容,varnish 服务器不缓存
if (req.http.Cache-Control ~ "no-cache" || req.http.Cache-Control ~ "private") {
return (pass);
}
#DO cache this ajax request
if(req.http.X-Requested-With == "XMLHttpRequest" && req.url ~ "recent_reviews") {
return (lookup);
}
#Dont cache ajax requests
if(req.http.X-Requested-With == "XMLHttpRequest" || req.url ~ "nocache" || req.url ~ "(login.php|register.php)")
{
return (pass);
}
if (req.request != "GET" &&
req.request != "HEAD" &&
req.request != "PUT" &&
req.request != "POST" &&
req.request != "TRACE" &&
req.request != "OPTIONS" &&
req.request != "DELETE") {
#/* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird.*/
return (pipe);
}
if (req.request != "GET" && req.request != "HEAD") {
#/* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */
return (pass);
}
#对请求中有验证及cookie,直接转发给后端服务器
if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) {
#/* Not cacheable by default */
return (pass);
}
return (lookup);
}
#
sub vcl_pipe {
# # Note that only the first request to the backend will have
# # X-Forwarded-For set. If you use X-Forwarded-For and want to
# # have it set for all requests, make sure to have:
# # set bereq.http.connection = "close";
# # here. It is not set by default as it might break some broken web
# # applications, like IIS with NTLM authentication.
return (pipe);
}
#
sub vcl_pass {
return (pass);
}
sub vcl_hash {
hash_data(req.url);
if (req.http.host) {
hash_data(req.http.host);
} else {
hash_data(server.ip);
}
return (hash);
}
sub vcl_hit {
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_miss {
return (fetch);
}
sub vcl_fetch {
if (beresp.ttl <= 0s ||
beresp.http.Set-Cookie ||
beresp.http.Vary == "*") {
#/*
# * Mark as "Hit-For-Pass" for the next 2 minutes
# */
set beresp.ttl = 120 s;
return (hit_for_pass);
}
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_deliver {
set resp.http.x-hits = obj.hits;
if (obj.hits > 0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "Hit this";
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "Miss this";
}
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_error {
set obj.http.Content-Type = "text/html; charset=utf-8";
set obj.http.Retry-After = "5";
synthetic {"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>"} + obj.status + " " + obj.response + {"</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Error "} + obj.status + " " + obj.response + {"</h1>
<p>"} + obj.response + {"</p>
<h3>Guru Meditation:</h3>
<p>XID: "} + req.xid + {"</p>
<hr>
<p>Varnish cache server</p>
</body>
</html>
"};
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_init {
return (ok);
}
sub vcl_fini {
return (ok);
}
处理缓存的样例 PHP 代码
<?php
// http header头信息中的 Cache-Control: s-maxage 参数可以设置页面在varnish中缓存的时间
// Cache-Control: max-age 参数可以设置本地浏览器的缓存时间
// Emit headers before any other content
//
cache_control( "public,max-age=10,s-maxage=10");
expires( to_gmt( time() + 10 ) );
?>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<?
print to_gmt();
?>
</body>
</html>
<?php
function to_gmt( $now = null ) {
return gmdate( 'D, d M Y H:i:s', ( $now == null ) ? time() : $now );
}
function last( $gmt ) {
header("Last Modified: $gmt");
}
function expires( $gmt ) {
header("Expires: $gmt");
}
function cache_control( $options ) {
header("Cache-Control: $options");
}
?>
header("Cache-Control: public,max-age=10,s-maxage=10,must-revalidate");
header('Last-Modified: ' . gmdate("D, d M Y H:i:s") . ' GMT');
header('Expires: ' . gmdate ("D, d M Y H:i:s", time() + 10). " GMT");
声明: 此文观点不代表本站立场;转载须要保留原文链接;版权疑问请联系我们。