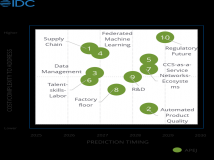
set @id = 10;call pr_param_in(@id);select @id as id_out;mysql> call pr_param_in(@id);+----------+| id_inner |+----------+| 11 |+--
set @id = 10;
call pr_param_in(@id);
select @id as id_out;
mysql> call pr_param_in(@id);
+----------+
| id_inner |
+----------+
| 11 |
+----------+
mysql> select @id as id_out;
+--------+
| id_out |
+--------+
| 10 |
+--------+
可以看到:用户变量 @id 传入值为
10,执行存储过程后,在过程内部值为:11(id_inner),但外部变量值依旧为:10(id_out)。
二、MySQL 存储过程参数(out)
MySQL 存储过程 “out” 参数:从存储过程内部传值给调用者。在存储过程内部,该参数初始值为
null,无论调用者是否给存储过程参数设置值。
drop procedure if exists pr_param_out;
create procedure pr_param_out
(
out id int
)
begin
select id as id_inner_1; -- id 初始值为 null
if (id is not null) then
set id = id + 1;
select id as id_inner_2;
else
select 1 into id;
end if;
select id as id_inner_3;
end;
set @id = 10;
call pr_param_out(@id);
select @id as id_out;
mysql> set @id = 10;
mysql>
mysql> call pr_param_out(@id);
+------------+
| id_inner_1 |
+------------+
| NULL |
+------------+
+------------+
| id_inner_3 |
+------------+
| 1 |
+------------+
mysql> select @id as id_out;
+--------+
| id_out |
+--------+
| 1 |
+--------+
可以看出,虽然我们设置了用户定义变量 @id 为 10,传递 @id 给存储过程后,在存储过程内部,id 的初始值总是
null(id_inner_1)。最后 id 值(id_out = 1)传回给调用者。
三、MySQL 存储过程参数(inout)
MySQL 存储过程 inout 参数跟 out 类似,都可以从存储过程内部传值给调用者。不同的是:调用者还可以通过
inout
参数传递值给存储过程。
drop procedure if exists pr_param_inout;
create procedure pr_param_inout
(
inout id int
)
begin
select id as id_inner_1; -- id 值为调用者传进来的值
if (id is not null) then
set id = id + 1;
select id as id_inner_2;
else
select 1 into id;
end if;
select id as id_inner_3;
end;
set @id = 10;
call pr_param_inout(@id);
select @id as id_out;
mysql> set @id = 10;
mysql>
mysql> call pr_param_inout(@id);
+------------+
| id_inner_1 |
+------------+
| 10 |
+------------+
+------------+
| id_inner_2 |
+------------+
| 11 |
+------------+
+------------+
| id_inner_3 |
+------------+
| 11 |
+------------+
mysql>
mysql> select @id as id_out;
+--------+
| id_out |
+--------+
| 11 |
+--------+
从结果可以看出:我们把 @id(10),传给存储过程后,存储过程最后又把计算结果值
11(id_inner_3)传回给调用者。
MySQL 存储过程 inout 参数的行为跟 C 语言函数中的引用传值类似。
通过以上例子:如果仅仅想把数据传给 MySQL 存储过程,那就使用“in” 类型参数;如果仅仅从 MySQL
存储过程返回值,那就使用“out” 类型参数;如果需要把数据传给 MySQL
存储过程,还要经过一些计算后再传回给我们,此时,要使用“inout” 类型参数。
call pr_param_in(@id);
select @id as id_out;
mysql> call pr_param_in(@id);
+----------+
| id_inner |
+----------+
| 11 |
+----------+
mysql> select @id as id_out;
+--------+
| id_out |
+--------+
| 10 |
+--------+
可以看到:用户变量 @id 传入值为
10,执行存储过程后,在过程内部值为:11(id_inner),但外部变量值依旧为:10(id_out)。
MySQL 存储过程 “out” 参数:从存储过程内部传值给调用者。在存储过程内部,该参数初始值为
null,无论调用者是否给存储过程参数设置值。
create procedure pr_param_out
(
out id int
)
begin
select id as id_inner_1; -- id 初始值为 null
if (id is not null) then
set id = id + 1;
select id as id_inner_2;
else
select 1 into id;
end if;
select id as id_inner_3;
end;
set @id = 10;
call pr_param_out(@id);
select @id as id_out;
mysql> set @id = 10;
mysql>
mysql> call pr_param_out(@id);
+------------+
| id_inner_1 |
+------------+
| NULL |
+------------+
+------------+
| id_inner_3 |
+------------+
| 1 |
+------------+
mysql> select @id as id_out;
+--------+
| id_out |
+--------+
| 1 |
+--------+
可以看出,虽然我们设置了用户定义变量 @id 为 10,传递 @id 给存储过程后,在存储过程内部,id 的初始值总是
null(id_inner_1)。最后 id 值(id_out = 1)传回给调用者。
MySQL 存储过程 inout 参数跟 out 类似,都可以从存储过程内部传值给调用者。不同的是:调用者还可以通过
inout
参数传递值给存储过程。
create procedure pr_param_inout
(
inout id int
)
begin
select id as id_inner_1; -- id 值为调用者传进来的值
if (id is not null) then
set id = id + 1;
select id as id_inner_2;
else
select 1 into id;
end if;
select id as id_inner_3;
end;
set @id = 10;
call pr_param_inout(@id);
select @id as id_out;
mysql> set @id = 10;
mysql>
mysql> call pr_param_inout(@id);
+------------+
| id_inner_1 |
+------------+
| 10 |
+------------+
+------------+
| id_inner_2 |
+------------+
| 11 |
+------------+
+------------+
| id_inner_3 |
+------------+
| 11 |
+------------+
mysql>
mysql> select @id as id_out;
+--------+
| id_out |
+--------+
| 11 |
+--------+
从结果可以看出:我们把 @id(10),传给存储过程后,存储过程最后又把计算结果值
11(id_inner_3)传回给调用者。
MySQL 存储过程 inout 参数的行为跟 C 语言函数中的引用传值类似。
通过以上例子:如果仅仅想把数据传给 MySQL 存储过程,那就使用“in” 类型参数;如果仅仅从 MySQL
存储过程返回值,那就使用“out” 类型参数;如果需要把数据传给 MySQL
存储过程,还要经过一些计算后再传回给我们,此时,要使用“inout” 类型参数。
声明: 此文观点不代表本站立场;转载须要保留原文链接;版权疑问请联系我们。